
December 18, 2019 -
Non-communicable diseasesalso known as chronic diseases are not transmissible directly from one person to another. Cardiovascular diseases account for most NCD deaths annually, followed by cancers, respiratory diseases, and diabetes. NCDs kill 41 million people each year, equivalent to 71% of all deaths globally.
NCDs include also Parkinson disease, autoimmune diseases, strokes, chronic kidney disease, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, Alzheimer's disease, cataracts, and others.
Detection, screening and treatment of NCDs, as well as palliative care, are key components of the response to NCDs.
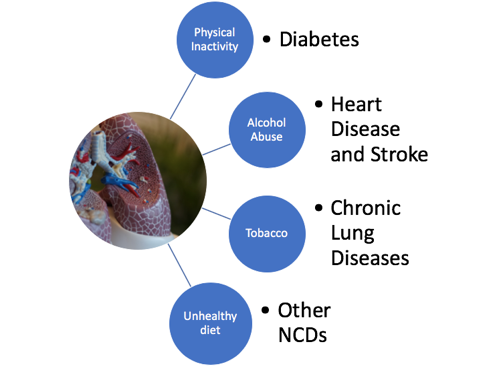
People of all age groups, regions and countries are affected by NCDs. These conditions are often associated with older age groups, but evidence shows that 15 million of all deaths attributed to NCDs occur between the ages of 30 and 69 years. Of these "premature" deaths, over 85% are estimated to occur in low- and middle-income countries. Children, adults and the elderly are all vulnerable to the risk factors contributing to NCDs, whether from unhealthy diets, physical inactivity, exposure to tobacco smoke or the harmful use of alcohol.
Behavioural risk factors
Modifiable behaviours, such as tobacco use, physical inactivity, unhealthy diet and the harmful use of alcohol, all increase the risk of NCDs.
Metabolic risk factors
Metabolic risk factors contribute to four key metabolic changes that increase the risk of NCDs:
In terms of attributable deaths, the leading metabolic risk factor globally is elevated blood pressure (to which 19% of global deaths are attributed), followed by overweight and obesity and raised blood glucose.
An important way to control NCDs is to focus on reducing the risk factors associated with these diseases. Low-cost solutions exist for governments and other stakeholders to reduce the common modifiable risk factors. Monitoring progress and trends of NCDs and their risk is important for guiding policy and priorities.
(Source: World Health Organization – WHO)
Digital Health is able to address NCDs to accelerate Universal Health Coverage (UHC) in LMICs.
Digital technology is revolutionizing healthcare delivery. Worldwide, digital tools are leading to better and faster healthcare – healthcare that is more empowering and accessible for patients, more client for providers and more cost effective for health systems.
In fact, digital health is probably the most powerful enabler that low- and middle- income communities can use to address the growing burden of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) and achieve universal health coverage. Ensuring all people can access the health services financial support is essential to achieving resilient communities – communities that are prepared for evolving health threats and enjoy greater economic prosperity thanks to healthier and more productive workforces.
There is much policymakers can do to create favorable environments for sustainable digital health, and they don't have to do it alone. Six building blocks can help countries realize the promise of digital health and transform access to appropriate, effective NCD care.

(source: Broadband Commission for Sustainable Development)
Although the World Health Organization recommends not to use telemedicine for a patient – doctor intervention, innovative web-based telemedicine platforms bring healthcare from hospitals into communities and remote places; connecting nurses and health workers.
Clinical decision-making with the support of web-based telemedicine platforms such as Case.io from Klughammer GmbH bring efficient communication and information to healthcare providers where needed most. Case.io is also useful where training of health personnel is needed.
NCD Alliance convened on 11 and 12 June 2019 in Dakar, Senegal, a meeting to discuss the opportunities offered by digital technologies in the NCD response.
The meeting, supported by Novartis Foundation, was attended by key actors involved in the fight against NCDs in Senegal. It discussed mobilization and coordination of stakeholders around good practice to promote the implementation of sustainable digital health solutions for NCDs and sustainable financing models.